Hieff Trans™ in vitro siRNA/miRNA Transfection Reagent
Product Description
Hieff Trans™ siRNA/miRNA in Vitro Transfection Reagent can achieve over 90% expression efficiency of 1 nM siRNA in a wide range of cell lines, avoiding off-target effects. Suitable for transfection of a variety of cells, including Hela, MCF-7, HepG2, CHO, and other adherent cells; and difficult-to-transfect suspension cell lines, such as K562 or THP-1 cells, can achieve 80% silencing efficiency; Including some primary cells, primary human fibroblasts, and primary human hepatocytes, etc., the silencing efficiency of 80% can be achieved.
Shipping and Storage
The product is shipped with ice packs and can be stored at 2-8ºC for one year. Do not freeze!
Cautions
1) Use RNase-free and non-pyrogenic materials throughout the experiment, such as centrifuge tubes, pipette tips, and buffers.
2) Before transfection, make sure that the siRNA has been purified by PAGE and desalted. High-purity siRNA or miRNA helps to obtain higher transfection efficiency.
3) The PEI cationic transfection reagent should be stored at 4 ºC, and care should be taken to avoid repeatedly opening the lid for a long time, otherwise, it may cause PEI to volatilize and reduce the transfection efficiency.
4) One day before transfection, make sure that the density of adherent cells is around 30%-50%. For some small cells and slow-growing cells, the density can be appropriately increased by 2 times.
5) Before transfection, ensure that siRNA/miRNA gene silencing expression will not affect cell viability.
6) This product is only suitable for in vitro transfection and can not be used for in vivo transfection.
7) For research use only!
Instructions
1 Transfection of adherent cells (take 24-well plate and transfection of 1 nM siRNA as an example, please refer to Table 1 for the loading volume of other culture plates)
seeding adherent cells
1.1 In order to improve the transfection efficiency, it is recommended to inoculate the cells one day before the transfection. The density of the inoculated cells is recommended to be about 30%-50%. It is recommended to set a gradient to optimize the optimal usage amount when using it for the first time.
1.2 Prepare the cationic complex of siRNA-PEI or miRNAPEI sub-nucleic acid transfection reagent according to the following system:
1) For each well of cells, dilute 8.4 ng of siRNA (0.6 pmoles) with 100 μL of serum-free medium (such as OPTI-MEM I medium) and mix well.
2) Immediately add 2 μL of transfection reagent to 100 μL of siRNA, vortex for 10 seconds, and mix well.
3) Incubate at room temperature for 10 min to form the siRNA-PEI cationic nucleic acid transfection reagent complex.
[Note] The incubation time should not exceed 30min
4) During complex formation, remove the cell growth medium and add 500 μL of fresh prewarmed complete medium to each well.
5) Add 100 µL of siRNA-PEI cationic nucleic acid transfection reagent complex directly into the cells, shake the culture plate, and mix gently. The final volume is 600 µL and the final siRNA concentration is 1 nM.
6) Cultivate at 37°C, 5% CO2 incubator until the target gene is expressed. It is suggested that the general mRNA expression level is usually 24-72 h, and the protein expression level is 48-96 h.
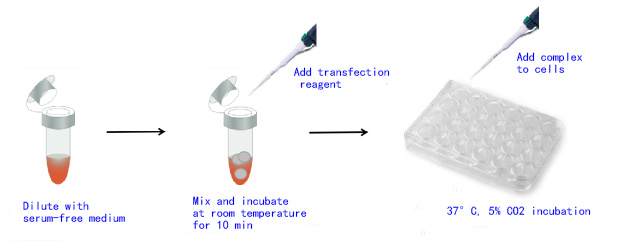
Figure 1. Procedure for transfection of adherent cells
[Note]: The transfection efficiency of siRNA will be affected by factors such as target gene, cell type, siRNA titer, the half-life of target mRNA, and the turnover rate of the target protein. The recommended siRNA concentration is between 1 nM and 10 nM. The volume of transfection reagent should be adjusted according to the siRNA concentration and the size of the petri dish, see Table 1 below.
Table 1. When the final concentration of siRNA is 1 nM, the reference value of the dosage of transfection reagent and medium
|
Culture vessel |
Surf. area per well 1 (cm2) |
siRNA (pmoles) |
Amount of siRNA per well(ng) |
Transfection reagent(μL) |
Vol. of dilution medium 2(μL) |
Vol. of plating medium |
|
96-well |
0.3 |
0.17 |
2.4 |
0.7-0.8 |
50 |
175 μL |
|
24-well |
1.9 |
0.6 |
8.6 |
1-3 |
100 |
600 μL |
|
12-well |
3.8 |
1.2 |
17 |
2-6 |
200 |
1.2 mL |
|
6-well |
10 |
2.2 |
31 |
4-12 |
200 |
2.2 mL |
|
Flask 25cm2 |
21 |
4.4 |
62 |
10-20 |
400 |
4.4 mL |
|
Flask 75cm2 |
58 |
10.5 |
147 |
30-50 |
500 |
10.5 mL |
1. The surface area of cell culture plates provided by different manufacturers may vary;
2. Volume of the medium used to dilute complexation.
Table 2. When the final concentration of siRNA is 10 - 50 nM, the reference value of the dosage of transfection reagent and medium
|
Culture vessel |
Surf. area per well 1 (cm2) |
Transfection reagent(μL) |
Vol. of dilution medium 2(μL) |
Vol. of plating medium |
|
96-well |
0.3 |
0.5-1.5 |
50 |
175 μL |
|
24-well |
1.9 |
2-4 |
100 |
600 μL |
|
12-well |
3.8 |
4-6 |
200 |
1.2 mL |
|
6-well |
10 |
8-16 |
200 |
2.2 mL |
|
Flask 25cm2 |
21 |
15-25 |
400 |
4.4 mL |
1. The surface area of cell culture plates provided by different manufacturers may vary;
2. Volume of the medium used to dilute complexation.
2 Suspension cell transfection (take 24-well plate and transfection of 5 nM siRNA as an example, please refer to Table 4 for the loading volume of other culture plates)
seeded cells
2.1 To optimize transfection conditions for suspension cells, the volume of medium for suspension cells needs to be reduced compared to adherent cells. Depending on the dish size and the volume of the complete medium, the recommended number of cells to seed in suspension is shown in Table 3 below.
Table 3. On the day of transfection, according to the size of the culture dish, the reference value of the number of cells inoculated in the suspension
|
Culture vessel |
Surf. area per well 1 (cm2) |
Vol. of cell (μL) |
Cell number |
|
384-well |
0.1 |
25 |
5×103-1×104 |
|
96-well |
0.3 |
50 |
1×104-2×104 |
|
24-well |
1.9 |
200 |
1×105-2×105 |
|
12-well |
3.8 |
500 |
2×105-4×105 |
|
6-well |
10 |
1000 |
5×105-2×106 |
|
Flask 25cm2 |
21 |
2000 |
2×106-5×106 |
1. The surface area of cell culture plates provided by different manufacturers may vary;
2.2 Prepare the siRNA-PEI cationic nucleic acid transfection reagent complex according to the following system:
1) For each well of cells, dilute 21 ng siRNA (1.5 pmols) with 100 μL of serum-free medium (such as OPTI-MEM I medium) and mix well.
2) Add 4 μL of transfection reagent to 100 μL of siRNA, vortex immediately for 10 seconds, and mix well.
3) Incubate for 15 min at room temperature to form the siRNA-PEI cationic nucleic acid transfection reagent complex.
[Note] The incubation time should not exceed 30 min
4) Add 100 μL of siRNA-PEI cationic nucleic acid transfection reagent complex to 200 μL of cell suspension in each well, and mix gently. The final volume is 300 µL, and the final siRNA concentration is 5 nM.
5) After culturing for 4-6 hours in a 37 ℃, 5% CO2 incubator, add 700 µL of complete medium, and gently shake the culture plate to mix.
6) Continue to incubate in the incubator until the target gene is expressed. It is suggested that the general mRNA expression level is usually 24-72 h, and the protein expression level is 48-96 h.
Hieff TransTM in vitro siRNA-miRNA Transfection Reagent FAQ
(1) Q: What is the difference between DNA transfection and siRNA transfection?
A: 1.Since there are only 20 base pairs, siRNA is much smaller than DNA with thousands or even more than 10,000 base pairs.
2. The transfection reagents and methods used to transfect DNA are not suitable for transfection of siRNA.
3. siRNA transfection has stricter requirements on the cytotoxicity of transfection reagents than DNA transfection.
(2) Q: Does the transfection reagent need to be changed after transfection?
A: For the medium change, two situations can be distinguished:
1. If there is no medium change before transfection, the medium should be changed about 6 hours after transfection to ensure the nutrients needed for cell growth;
2. If there is a change before transfection The medium can be changed as usual when the medium is nutrient deficient.
(3) Q: What is the efficiency of PEI transfection reagent for transfecting siRNA and plasmid?
A: This PEI transfection reagent is specially developed for siRNA, and plasmid transfection is not recommended.
(4) Q: Can the transfection reagent be frozen?
A: Do not freeze, because the transfection reagent is a PEI cationic transfection reagent. Freezing at low temperature will destroy the activity of the PEI transfection reagent. Therefore, it is best to store it at 4 degrees to maintain the best transfection efficiency.
(5) Q: How to improve the transfection efficiency?
A: a: Density of cells at the time of transfection, 30%-50%.
b: Opti-MEM serum-free medium should be used for siRNA and liposome dilution during transfection.
c: The medium can be changed 4-6h after transfection.
[1] Zhang Y, Hu R, Xi B, Nie D, Xu H, Liu A. Mechanisms of Senescence-Related NKG2D Ligands Release and Immune Escape Induced by Chemotherapy in Neuroblastoma Cells. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022;10:829404. Published 2022 Mar 2. doi:10.3389/fcell.2022.829404(IF:6.684)
[2] Cui B, Wang Y, Jin J, et al. Resveratrol Treats UVB-Induced Photoaging by Anti-MMP Expression, through Anti-Inflammatory, Antioxidant, and Antiapoptotic Properties, and Treats Photoaging by Upregulating VEGF-B Expression. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2022;2022:6037303. Published 2022 Jan 4. doi:10.1155/2022/6037303(IF:6.543)
[3] Liu Y, Zeng Y, Si HB, Tang L, Xie HQ, Shen B. Exosomes Derived From Human Urine-Derived Stem Cells Overexpressing miR-140-5p Alleviate Knee Osteoarthritis Through Downregulation of VEGFA in a Rat Model. Am J Sports Med. 2022;50(4):1088-1105. doi:10.1177/03635465221073991(IF:6.203)
[4] Zhang ZD, Wen B, Li DJ, et al. AKT serine/threonine kinase 2-mediated phosphorylation of fascin threonine 403 regulates esophageal cancer progression. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2022;145:106188. doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2022.106188(IF:5.085)
[5] Tan S, Zhou Y, Zhao H, et al. Comprehensive transcriptome analysis of hypothalamus reveals genes associated with disorders of sex development in pigs. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2021;210:105875. doi:10.1016/j.jsbmb.2021.105875(IF:4.294)
[6] Niu M, Yi M, Dong B, Luo S, Wu K. Upregulation of STAT1-CCL5 axis is a biomarker of colon cancer and promotes the proliferation of colon cancer cells. Ann Transl Med. 2020;8(15):951. doi:10.21037/atm-20-4428(IF:3.297)
Catalog No.:*
Name*
phone Number:*
Lot:*
Email*
Country:*
Company/Institute:*

